ORGANISATION MAPPING TOOL: AT A GLANCE
There are two and a half lakh panchayats in India. Spends of over Rs. 400,000 crores are done in panchayats, impacting land, water and agricultural resources, education, health and social security covers. Panchayats are to govern 6 lakh villages, upholding democratic principles. However, impact of governance and return on funds is suboptimal. BECAUSE – most panchayat members are not aware of their powers and responsibilities.
Understanding begins with awareness, and change comes from understanding.
The Gram Panchayat Organisation mapping tool is designed to help panchayat members, citizens and any other stakeholder within a panchayat understand the identity and functioning of a Gram Panchayat. It simultaneously, enables refection and rating of the institutional status of a panchayat. Equipped with such understanding and rating, a GP may prioritise actions towards improvement of its functioning.
The salient features of the tool are:
- It comprises 9 key components that are reflect an effective GP, such as status of services, an empowered identity, clarity of vision, enabling structures, effective planning and budgeting processes etc.
- Includes relevant provisions of the legal framework of the state which panchayats are mandated to follow.
- Outputs of the tool are a) Ward wise status of services, b) ratings on remaining 8 components which are key for delivery of services and democratic governance, and c) a consolidated rating as a Panchayat Maturity level, all on scales of 1 to 4.
Who can use this app?
- Civil Society Organisation which wants to work towards building panchayat capacities: the tool will help develop panchayat specific engagement methodologies based on ratings across 9 components.
- Organisations engaged in improving sectoral indicators in rural India: Explore partnerships with institutionally mature GPs. You will have quicker and sustainable results and will also create role models.
- Any agency which wants to map and report the ‘Status of Panchayats’ as an input to creating panchayat curriculums and resources at State or National levels
- Gram Panchayats themselves, for reflection and self-assessment to plan their growth strategies.
ORGANISATION MAPPING TOOL: DESCRIPTION
Organization mapping (OM) is a self-assessment exercise that provides a platform for GP members to map their GP across several dimensions of an effective GP organisation, as well as how it stands vis-à-vis its roles and mandate as outlined in the legal framework of the state. The process is embedded in Anode’s Gram Panchayat Organisation Development (GPOD) framework, which focuses on enhancing effectiveness of panchayats as institutions. Once a panchayat understands its current status, the next GPOD step is to facilitate discussion on way forward, a visioning exercise which is a precursor to developing its plans and designing an appropriate organisation.
The OM tool is evidence-based, designed based on Anode's experience in working with 100 plus Gram Panchayats across 4 states (Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka & Maharashtra). The OM process is not an audit to arrive at a score card for participating panchayats. Rather, it needs to be facilitated through participative pedagogy conducted across multiple sessions.
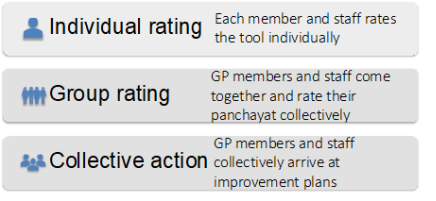
The process focuses on building knowledge and facilitating reflection among elected members and staff of a panchayat, first individually and subsequently, collectively.
Through engaging in this process, we hope participants will understand their own institution better and developing their own pathways for making it more effective. For facilitators working with panchayats, in addition to providing them with an in-depth understanding of the institution, the tool will help in designing continuous engagement with its members.
INPUTS
- GP profile: Location, Villages and Wards
-
Components: The tool is designed along 9 components, critical for effective GP functioning:
1. Identity & Vision
2. GP Structures
3. Service Delivery
4. Planning, Budgeting and Monitoring Implementation
5. Infrastructure management and Administration
6. Coordination between GP and Gram Sabha(s)
7. Management of Funds & Properties
8. Transparency in the GP
9. Disaster Management
All the components have further sub-components, which are key elements to understand and gauge the status of GP on that component, as derived from our experience across panchayats. -
Legal framework: There is a functionality to enter provisions from relevant Acts, Programs and Schemes that impact functioning of panchayats. Legal provisions are entered State-wise. This functionality is also to serve as a guide and knowledge repository for users.
The 9th component, Disaster management, was added in the tool in the context of prevailing CoVid pandemic -
Rating scales: Four different types of scales have been designed to ensure accurate mapping of different components and sub-components:
Straight Scales: The classic straight scale uses a 4-point response scale
Multiple scales in one: In case of sub-components which need to be understood and mapped across several dimensions, there are several parameters, each to be rated on a straight scale.
In all scales, the composite score is converted into rating on a 4-point scale for the sub-component.
OUTPUTS
-
GP’s overall institutional maturity level: The score for overall maturity level of a GP is an average score of all components. There are no weightages assigned to any component, as we believe it is the prerogative of the GP institution to assign less or more importance to different parameters. For instance, an institutional maturity level 3 denotes a panchayat which is operating as per the legal mandate set by the State. Brief descriptions are as follows:
Level 1: GP is not functioning as a unit of local government. It can make many improvements to serve its citizens.
Level 2: GP has potential to serve its citizens better. Needs to prepare a plan for improvement and start working on it.
Level 3: An effective GP which is serving its citizens well. With its capabilities, and with further collaborations, it can start impacting decision making at the block and district levels.
Level 4: GP is a role model. Many GPs can learn from its internal systems, levels of participation, service delivery, and contracts with external agencies. We look forward to seeing the further improvements you make that we can all learn from. - Ward wise status of services, as rated by respective elected members, and if extended further, by citizens
- Status on different organisation components: Rating on different organisational processes of a Gram Panchayat.
-
Suggested actions which a panchayat can take to move to higher levels of institutional maturity. Two types of actions are suggested: Quick actions and Medium to long term actions.
For e.g., if a GP scores a rating of 2 in the first component, Identity and Vision, it can initiate following actions:
Quick actions:
GP members need to undergo training on 73rd Amendment, the identity, functions and powers of a GP, as laid down in the Constitution.
Medium to long term actions:
GP needs to define its long-term vision, and goals for next 3-5 years - Dashboard reflecting coverage, different inter-GP comparisons. The dashboard will be expanded as more GPs use this tool and we gain further experience.